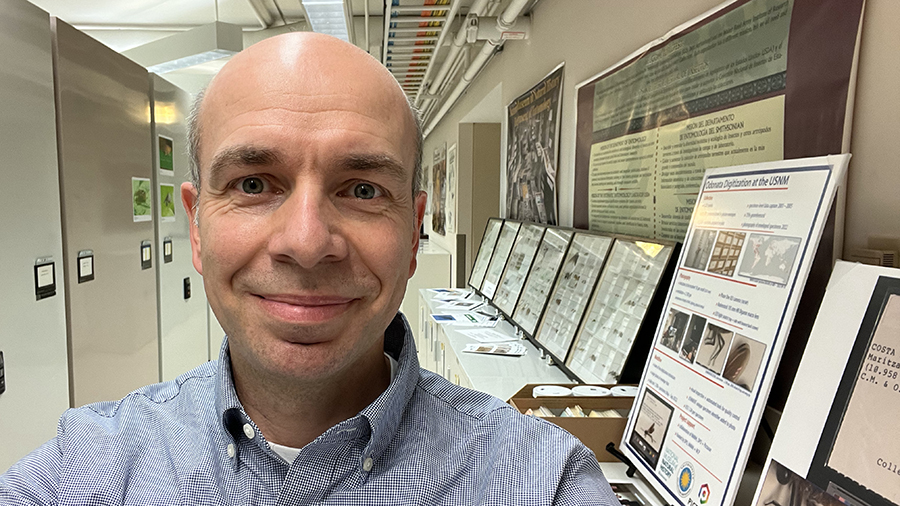
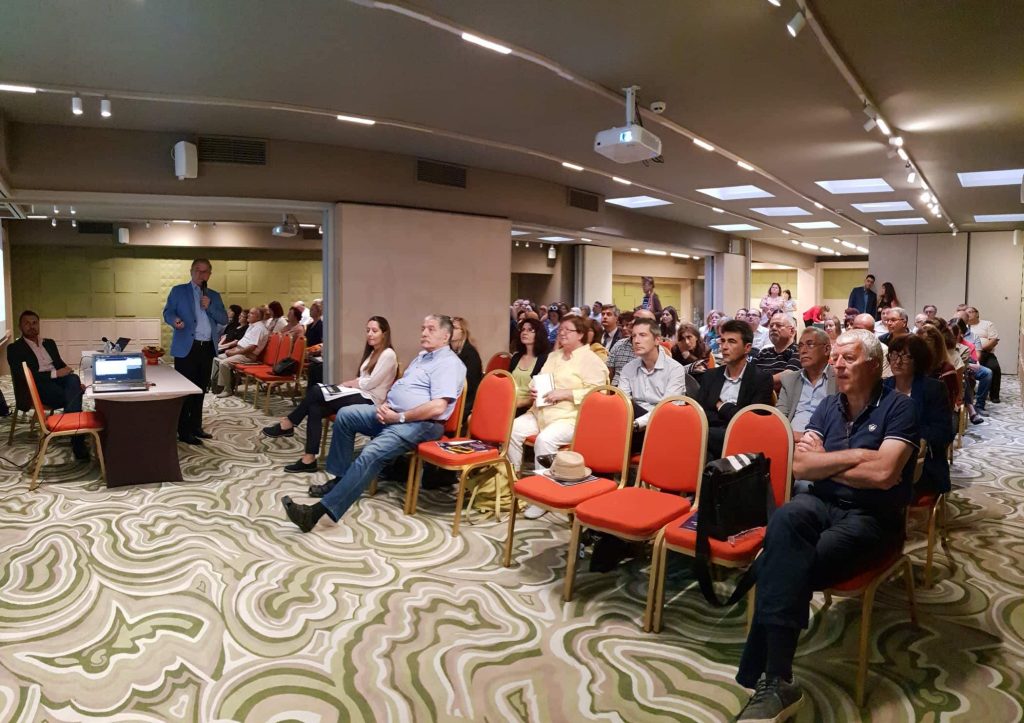
Esteemed entomologist specialising in true flies (order Diptera) and cybertaxonomy, Dr Torsten Dikow was appointed as the new Editor-in-Chief of the leading open-access peer-reviewed journal in systematic zoology and biodiversity ZooKeys.
Dikow is to step into the shoes of globally celebrated fellow entomologist and colleague at the Smithsonian and founding Editor-in-Chief of ZooKeys Dr Terry Erwin, who sadly passed away in May, 2020, leaving behind hefty scientific legacy and immeasurable admiration and fond memories.
Today, Dikow is a Research Entomologist and Curator of Diptera and Aquatic Insects at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History (Washington, DC, USA), where his research interests encompass the diversity and evolutionary history of the superfamily Asiloidea – or asiloid flies – comprising curious insect groups, such as the assassin flies / robber flies and the mydas flies. Amongst an extensive list of research publications, Dikow’s studies on the diversity, biology, distribution and systematics of asiloid flies include the description of 60 species of assassin flies alone, and the redescription of even more through comprehensive taxonomic revisions.
Dikow obtained his M.S. in Zoology from the Universität Rostock (Germany) and Ph.D. in Entomology from Cornell University (New York, USA) with three years of dissertation research conducted at the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH).
During his years as a postdoc at the Field Museum (Illinois, USA), Dikow was earnestly involved in the broader activities of the Encyclopedia of Life through its Biodiversity Synthesis Center (BioSynC) and the Biodiversity Heritage Library (BHL). There, he would personally establish contacts with smaller natural history museums and scientific societies, and encourage them to grant digitisation permissions to the BHL for in-copyright scientific publications. Dikow is a champion of cybertaxonomic tools and making biodiversity data accessible from both natural history collections and publications. He has been named a Biodiversity Open Data Ambassador by the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF).
Dikow is no stranger to ZooKeys and other journals published by the open-access scientific publisher and technology provider Pensoft. For the past 10 years, he has been amongst the most active editors and a regular author and reviewer at ZooKeys, Biodiversity Data Journal and African Invertebrates.
“Publishing taxonomic revisions and species descriptions in an open-access, innovative journal to make data digitally accessible is one way we taxonomists can and need to add to the biodiversity knowledge base. ZooKeys has been a journal in support of this goal since day one. I am excited to lend my expertise and enthusiasm to further this goal and continue the development to publish foundational biodiversity research, species discoveries, and much more in the zoological field,”
said Dikow.
Dikow took on his new role at ZooKeys at a time when the journal had just turned 15 years on the scholarly publishing scene. In late 2020, the scientific outlet also marked the publication of its 1000th journal volume.
***
Visit the journal’s website and follow ZooKeys on X (formerly Twitter) and Facebook. You can also follow Torsten Dikow on X.
***
About ZooKeys:

ZooKeys is a peer-reviewed, open-access, rapidly disseminated journal launched to accelerate research and free information exchange in taxonomy, phylogeny, biogeography and evolution of animals. ZooKeys aims to apply the latest trends and methodologies in publishing and preservation of digital materials to meet the highest possible standards of the cybertaxonomy era.
ZooKeys publishes papers in systematic zoology containing taxonomic/faunistic data on any taxon of any geological age from any part of the world with no limit to manuscript size. To respond to the current trends in linking biodiversity information and synthesising the knowledge through technology advancements, ZooKeys also publishes papers across other taxon-based disciplines, such as ecology, molecular biology, genomics, evolutionary biology, palaeontology, behavioural science, bioinformatics, etc.