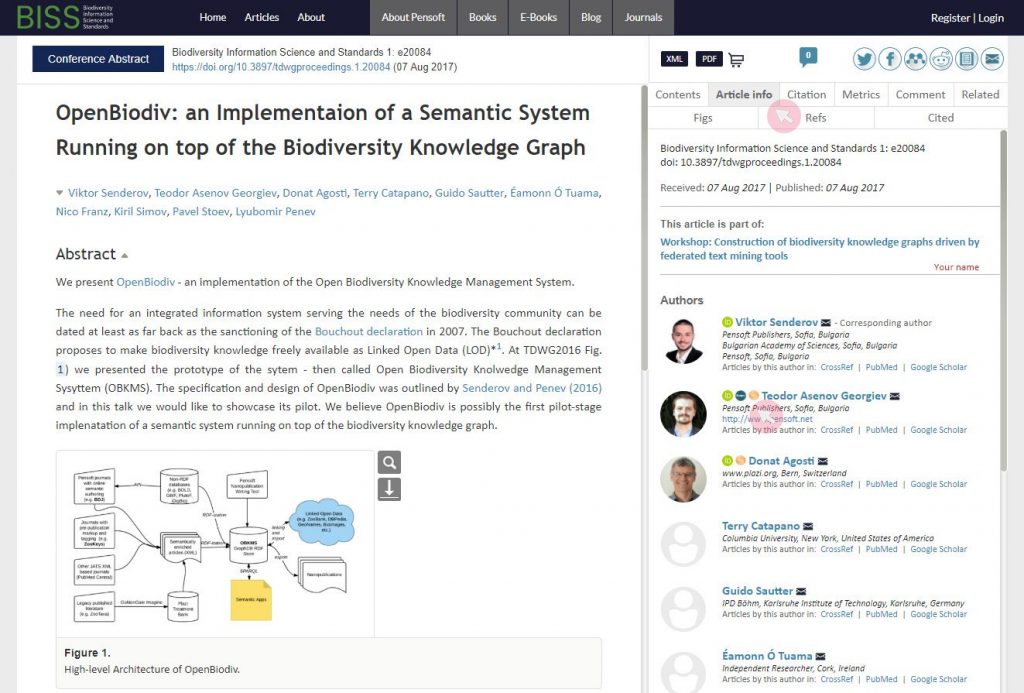
Partners GBIF, FinBIF and Pensoft to support publication of data papers that describe datasets from Russia west of the Ural Mountains
Original post via GBIF
GBIF—the Global Biodiversity Information Facility—in collaboration with the Finnish Biodiversity Information Facility (FinBIF) and Pensoft Publishers, are happy to issue a call for authors to submit and publish data papers on European Russia (west of the Urals) in an upcoming special issue of Biodiversity Data Journal (BDJ).
Between now and 31 August 2020, the article processing fee (normally €450) will be waived for the first 20 papers, provided that the publications are accepted and meet the following criteria that the data paper describes a dataset:
- with more than 5,000 records that are new to GBIF.org in 2020
- with high-quality data and metadata
- with geographic coverage in European Russia west of the Ural mountains
The manuscript must be prepared in English and is submitted in accordance with BDJ’s instructions to authors by 31 August 2020. Late submissions will not be eligible for APC waivers.
Sponsorship is limited to the first 20 accepted submissions meeting these criteria on a first-come, first-served basis. The call for submissions can therefore close prior to the stated deadline of 31 August. Authors may contribute to more than one manuscript, but artificial division of the logically uniform data and data stories, or “salami publishing”, is not allowed.
BDJ will publish a special issue including the selected papers by the end of 2020. The journal is indexed by Web of Science (Impact Factor 1.029), Scopus (CiteScore: 1.24) and listed in РИНЦ / eLibrary.ru
For non-native speakers, please ensure that your English is checked either by native speakers or by professional English-language editors prior to submission. You may credit these individuals as a “Contributor” through the AWT interface. Contributors are not listed as co-authors but can help you improve your manuscripts.
In addition to the BDJ instruction to authors, it is required that datasets referenced from the data paper a) cite the dataset’s DOI and b) appear in the paper’s list of references.
Authors should explore the GBIF.org section on data papers and Strategies and guidelines for scholarly publishing of biodiversity data. Manuscripts and datasets will go through a standard peer-review process.
To see an example, view this dataset on GBIF.org and the corresponding data paper published by BDJ.
Questions may be directed either to Dmitry Schigel, GBIF scientific officer, or Yasen Mutafchiev, managing editor of Biodiversity Data Journal.
Definition of terms
Datasets with more than 5,000 records that are new to GBIF.org
Datasets should contain at a minimum 5,000 new records that are new to GBIF.org. While the focus is on additional records for the region, records already published in GBIF may meet the criteria of ‘new’ if they are substantially improved, particularly through the addition of georeferenced locations.
Justification for publishing datasets with fewer records (e.g. sampling-event datasets, sequence-based data, checklists with endemics etc.) will be considered on a case-by-case basis.
Datasets with high-quality data and metadata
Authors should start by publishing a dataset comprised of data and metadata that meets GBIF’s stated data quality requirement. This effort will involve work on an installation of the GBIF Integrated Publishing Toolkit.
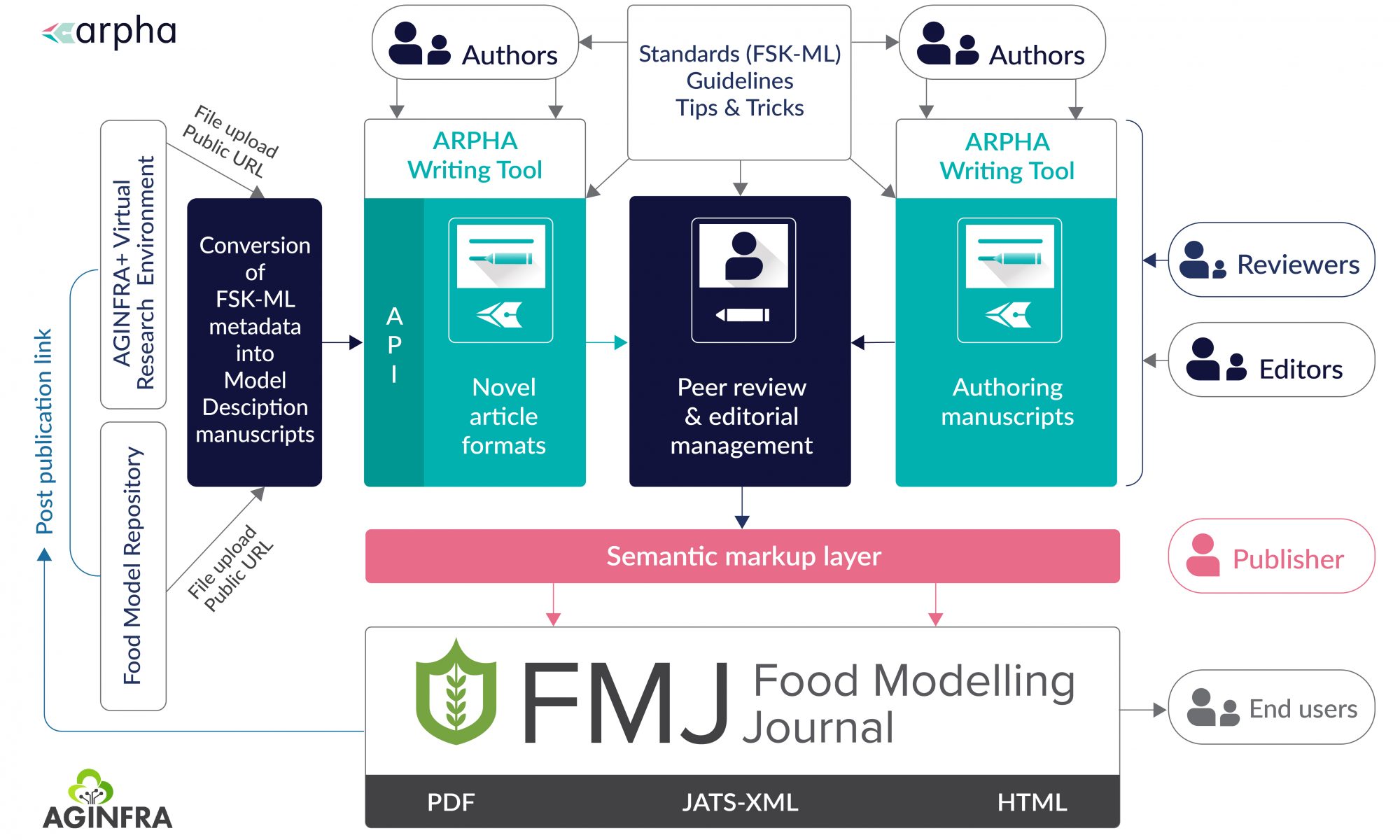
Only when the dataset is prepared should authors then turn to working on the manuscript text. The extended metadata you enter in the IPT while describing your dataset can be converted into manuscript with a single-click of a button in the ARPHA Writing Tool (see also Creation and Publication of Data Papers from Ecological Metadata Language (EML) Metadata. Authors can then complete, edit and submit manuscripts to BDJ for review.
Datasets with geographic coverage in European Russia west of the Ural mountains
In correspondence with the funding priorities of this programme, at least 80% of the records in a dataset should have coordinates that fall within the priority area of European Russia west of the Ural mountains. However, authors of the paper may be affiliated with institutions anywhere in the world.
#####
Data audit at Pensoft’s biodiversity journals
Data papers submitted to Biodiversity Data Journal, as well as all relevant biodiversity-themed journals in Pensoft’s portfolio, undergo a mandatory data auditing workflow before being passed down to a subject editor.

https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2019-10/pp-aif101819.php.