New open-access book presents a comprehensive report on the remarkable ecosystems of the Koytendag nature reserve
Image by Atamyrat Veyisov
Situated in the extreme south-east of Turkmenistan: on the border with Uzbekistan and close to the border with Afghanistan, Koytendag presents one of the most distinct landscapes in Central Asia. Reaching elevations of up to 3,137 m, this is also the highest mountain in Turkmenistan.
Koytendag State Nature Reserve and its three Wildlife Sanctuaries: Hojapil, Garlyk and Hojaburjybelent, were established between 1986 and 1990 to protect and preserve the mountain ecosystem of the Koytendag region and maintain the ecological balance between the environment and increasing economic activities.
Since 2013, a series of scientific expeditions and assessments were coordinated and funded by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) to pave the way for the protection and preservation of the unique landscape and rare wildlife the site is recognised for.
As a result, the efforts of the conducted field studies of multidisciplinary international research teams are brought together in a comprehensive report, which is now openly available as an Advanced Book from the scientific publisher and technology provider Pensoft, edited by Geoff Welch (RSPB) and Prof. Pavel Stoev (National National Museum of Natural History of Bulgaria and Pensoft). Soon, the book will also be available in Russian.
The book is split into eight sections focused on different areas within the study of biodiversity: Flora, Surface dwelling invertebrates, Cave fauna, Fish, Amphibians, Reptiles, Birds and Mammals. An additional chapter is dedicated to the hydrogeology of the site because of its key role in supporting both the cave fauna and the local communities.
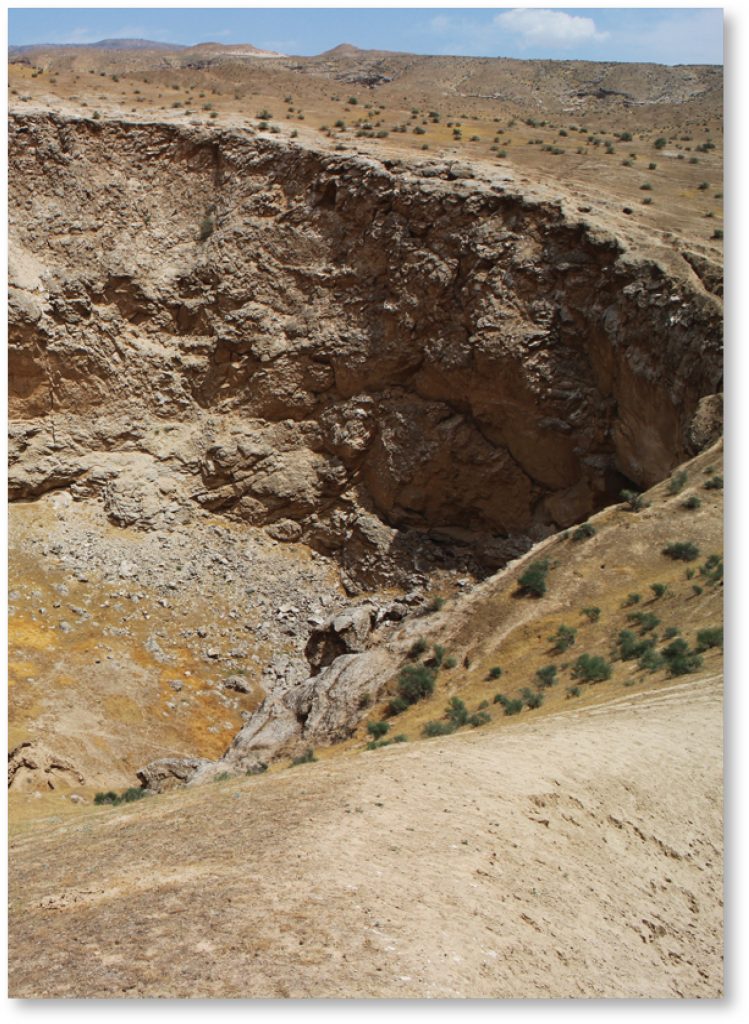

Photo by Mikhail Pereladov
In the summary of the report, the authors make a list of the most significant findings made during the research. These include the discovery of a cave hosting the largest underground lake in the whole North Eurasia (4,400 m2) and a total of 48 species of higher plants that can only be found in Koytendag. In terms of Koytendag’s surface-dwelling fauna, the report lists a number of species new to science: a scorpion (most likely yet unnamed species currently recognised as a species complex) and a spider. Meanwhile, a total of seven previously unknown species were found underground, including the very first exclusively subterranean animal found in the country: the insect-like ‘marvellous’ dipluran named Turkmenocampa mirabilis, and a strongly adapted to the underground waters of a desert sinkhole Gammarus troglomorphus. Additionally, the annual monitoring, conducted since 1995 by the reserve staff, report an encouraging increase in the populations of the rare markhors and mouflons. An intact predator-prey community was also identified as a result of observations of numerous Eurasian lynxes and grey wolves, as well as prey species.
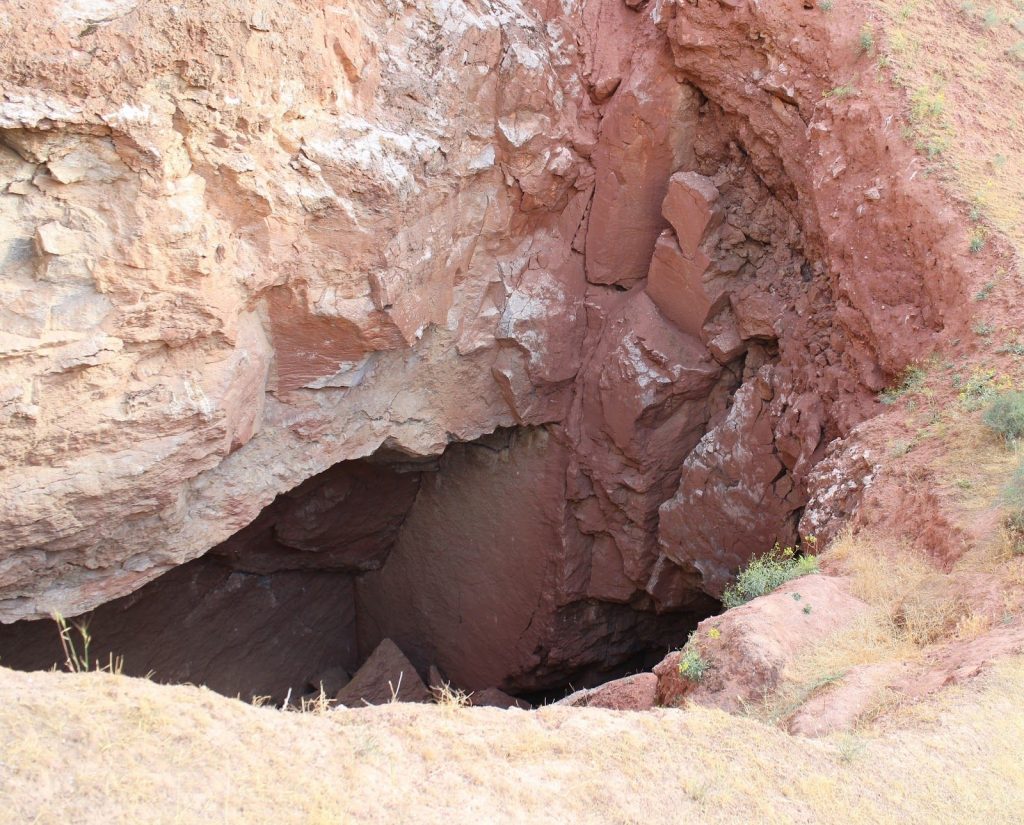

Photo by Aleksandr Degtyarev
Stephanie Ward, RSPB Central Asia Partner Development Officer, says:
“RSPB has been working in Turkmenistan under a Memorandum of Understanding with the Government since 2004. In that time we have had the privilege of working with a team of talented and dedicated national experts across the diverse and inspiring nature of this fascinating country. Our work in Koytendag has captured the attention and interest of many international scientists who hope that their contemporary biodiversity research will help to deepen the understanding and therefore ensure protection of the unique wonders of this mountain ecosystem. As a potential UNESCO World Heritage Site, we will continue to collaborate with the Turkmen people on the research and promotion of Koytendag State Nature Reserve.
Book editor and member of the research team Prof. Pavel Stoev adds:
“Koytendag Mountain is among the least explored and, simultaneously, one of the most biologically diverse regions in Central Asia. The rapid assessments of its flora and fauna revealed a high number of highly specialised species, all of which have undergone a long evolution to adapt to the harsh environments of the mountain. The establishment of Koytendag State Nature Reserve and the associated wildlife sanctuaries is a step in the right direction for the protection of this unique biota.”

https://doi.org/10.3897/ab.e37858.
###
Original source:
Welch G, Stoev P (2019) A report of RSPB-supported scientific research at Koytendag State Nature Reserve, East Turkmenistan. Advanced Books. https://doi.org/10.3897/ab.e37858
Additional information:
This work was carried out under the Memorandum of Understanding between the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment Protection of Turkmenistan and the RSPB, within the Project on “Improvement of the status of birds and other biodiversity in Turkmenistan”.
About Koytendag State Nature Reserve:
Koytendag State Nature Reserve was established in 1986 to protect and preserve the mountain ecosystem of the Koytendag region and maintain the ecological balance between the environment and the increasing anthropogenic activities. Of particular importance was the protection of rare species, such as the markhor; important habitats, including pistachio and juniper forests; and the impressive dinosaur trackways at Hojapil.
Advanced Books publishing by Pensoft:
Launched by Pensoft and powered by the scholarly publishing platform ARPHA, the Advanced Books approach aims to issue new books or re-issue books previously only available in print or PDF. In the Advanced Books format, the publications are semantically enhanced and available in HTML and XML as well, in order to accelerate open access, data publication, mining, sharing and reuse. The Advanced books builds on the novel approaches developed by the Pensoft’s journals.

