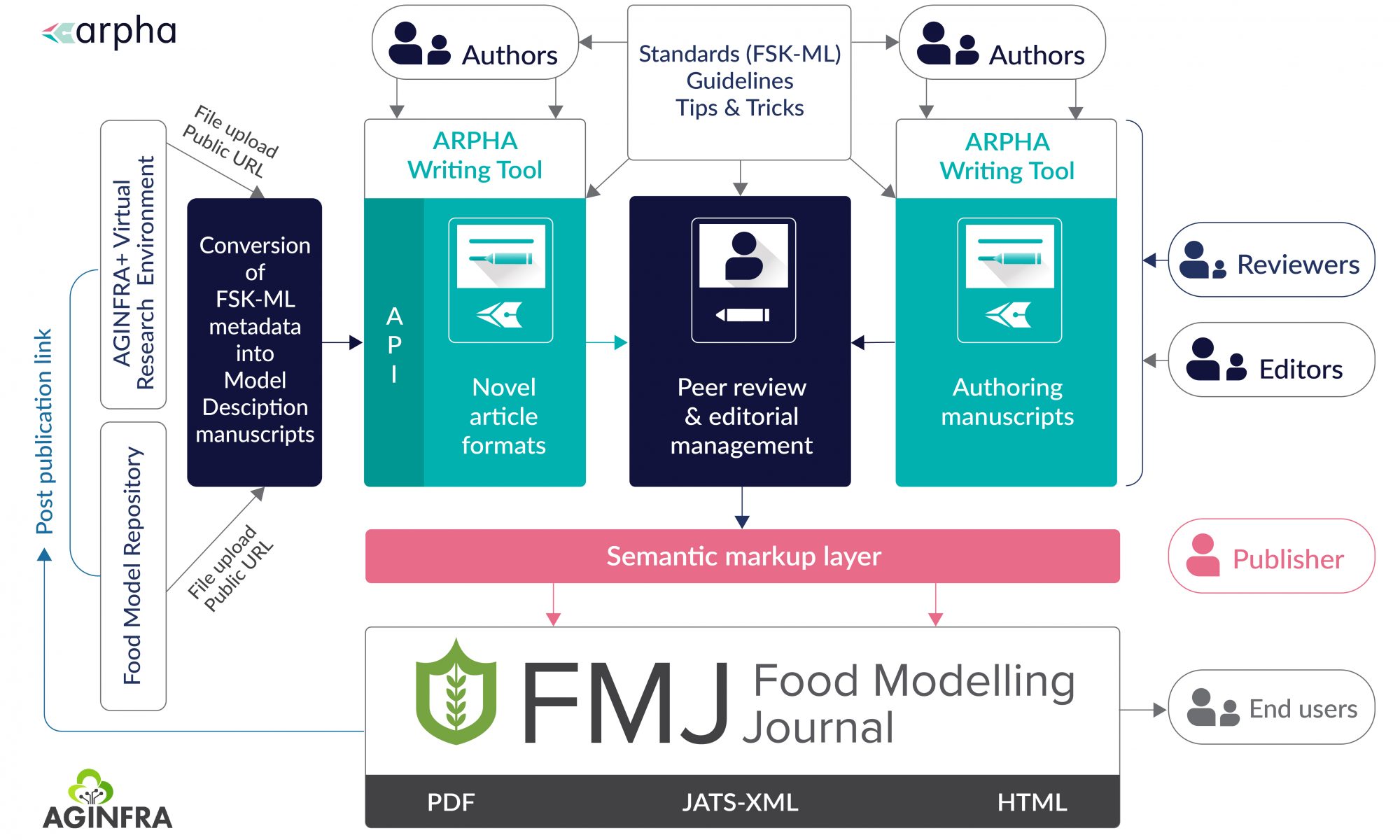
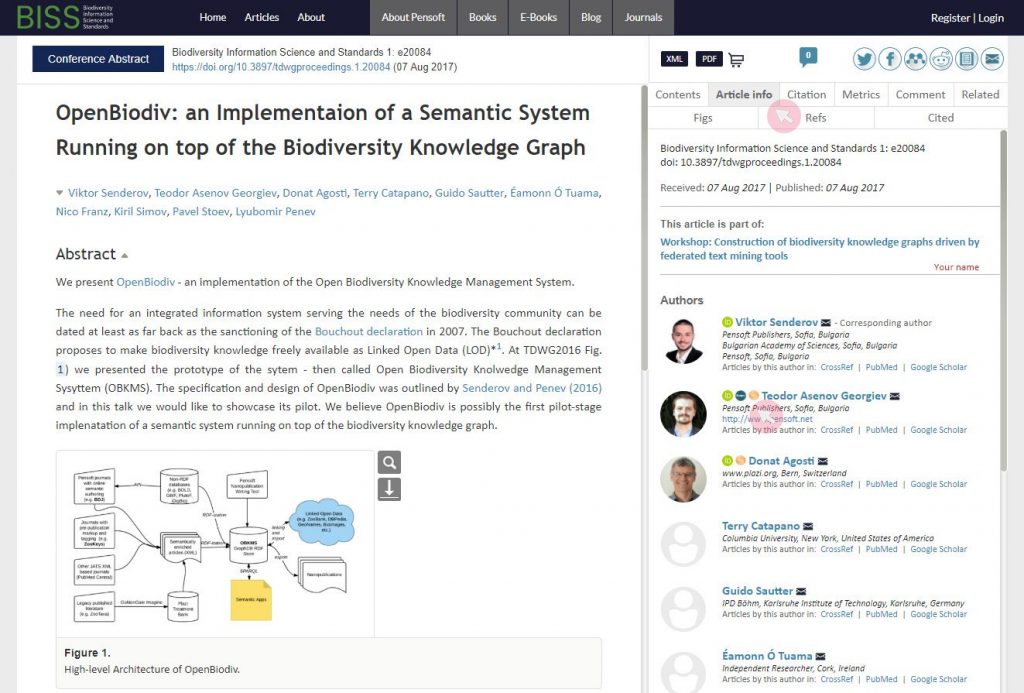
While Russia seems to have successfully tackled its historic problem: food shortage – with the agri-food sector becoming one of the most steadily developing of the national economy – the country is already facing a new set of challenges. Today, Russia needs to address several key growth factors, such as sustainability, missing national strategies and lagging research and development progress. These are the topics of the research articles comprising the latest special issue of the open-access peer-reviewed Russian Journal of Economics. An overview and introduction for the issue is provided by its guest editor Eugenia Serova of the Institute for Agrarian Studies at HSE University in Moscow.
Since 2012, Russia’s agriculture is the most steadily developing sector of the national economy. Production of selected crops is reaching historical records. Today, Russia is a world champion for export of wheat and buckwheat and amongst the top ten in terms of export of many other crops. The country has also begun exporting livestock products and value-added food products. Additionally, the past ten years have seen a significant progress in the food quality and safety in Russia, which has already been recognised. According to conventional indicators applied to food security, the country keeps a consistent place amongst the top three in the world.
However, even though Russia has been successful at achieving national food security, largely contributed to a strong emphasis on self-sufficiency, world known experts in food security at KU Leuven (Belgium) and International Food Policy Research Institute (USA) point out that this might have come at the expense of neglecting nutrition in the national policies, thus potentially exposing the nation at a higher risk of already concerning and quite common public health risks, such as malnourishment and obesity. In their paper, Saule Burkitbayeva, Johan Swinnen and Nele Warrinnier evaluate the state of art of food security in major Eurasian countries, in order to see where Russia stands compared to other former Soviet republics. The researchers also discuss the advantages and disadvantages of self-sufficiency policy.
Along with growth in the food sector in Russia, there have been drastic changes in the agrarian structure. With their profound analysis of two censuses from 2006 and 2016, recognised experts on Russia’s farming structure Renata Yanbykh and Valeriy Saraikin (both affiliated with the Institute for Agrarian Studies at HSE University, Moscow) and Zvi Lerman (The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel) conclude that the old classification used for statistical purposes (organisations, family farms and households) does not reflect adequately the dynamic changes stemming from the response to market signals. In their study, the authors find that over 90% of the agricultural producers contribute less than 5% of the total standard revenue.
A need to shift budget support to general services which support all Russian producers is highlighted in the research article by Olga V. Shik of the Institute for Agrarian Studies at HSE University. The renowned expert in the field conducts an exhaustive analysis of the public expenditures in the Russian agri-food sector from the last decade to conclude that despite having a positive effect on agricultural growth, Russia’s budget support benefits mostly the larger and already the most successful producers. The second major drawback of budget support in agriculture the author identifies is the inefficient distribution of support between the federal and regional budgets, which leads to market disintegration and reduces the efficiency of budget spending.
In their article, distinguished American experts on Russia’s agri-food trade William M. Liefert and Olga Liefert of the United States Department of Agriculture Economic Research Service (USDA ERS) report on how Russia’s move from planned to a market economy has fundamentally restructured the country’s agricultural production and trade since the 1990s. Most notably, previously a large importer of grain, soybeans, and soybean meal, the former Soviet state has transitioned to becoming one of the world’s major grain exporters. In fact, Russia has become the world’s top wheat exporter, responsible for 20-23% of the total world exports in 2017-2018. Having also discussed the consequences for the world agricultural markets, the researchers forecast further increase in Russia’s presence in the global market along with slight growth in its produce of value-added foods.
The last article, authored by researchers of the Institute for Agrarian Studies at HSE University Natalia Karlova and Eugenia Serova also addresses the issue of Russia’s presence in the world agri-food market with a focus on the trade with China. Since the significant increase in export is one of the major targets of Russia’s modern agri-food policy, China is seen as the most prospective market. However, there are a number of obstacles and risks that need to be taken into consideration. On one hand, Russia has a fairly limited list of exported agri-food products that have comparative advantages in the Chinese market. On the other hand, the Chinese market is limited by the scale of the country’s domestic demand. Moreover, China has already embarked on a course to self-sufficiency in terms of staple food produce.
###
Original sources:
Burkitbayeva S, Swinnen J, Warrinnier N (2020) Food and nutrition security in Eurasia: Evolution, shocks and policies. Russian Journal of Economics 6(1): 6-25. https://doi.org/10.32609/j.ruje.6.49749
Yanbykh R, Saraikin V, Lerman Z (2020) Changes in Russia’s agrarian structure: What can we learn from agricultural census? Russian Journal of Economics 6(1): 26-41. https://doi.org/10.32609/j.ruje.6.49746
Shik OV (2020) Public expenditure for agricultural sector in Russia: Does it promote growth? Russian Journal of Economics 6(1): 42-55. https://doi.org/10.32609/j.ruje.6.49756
Liefert WM, Liefert O (2020) Russian agricultural trade and world markets. Russian Journal of Economics 6(1): 56-70. https://doi.org/10.32609/j.ruje.6.50308
Karlova N, Serova E (2020) Prospects of the Chinese market for Russian agri-food exports. Russian Journal of Economics 6(1): 71-90. https://doi.org/10.32609/j.ruje.6.50824